Hidden Windows Caches & How to Clear Them
 1. The Windows 10 Update Cache
1. The Windows 10 Update Cache
Windows maintains a cache of Windows Updates files which are really not needed but take up a lot of space.
But before you delete these files it is best to temporarily stop the Windows Update service. To do this execute this command from a command prompt.
net stop wuauserv
Once that is done open the file directory: C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution\Download. 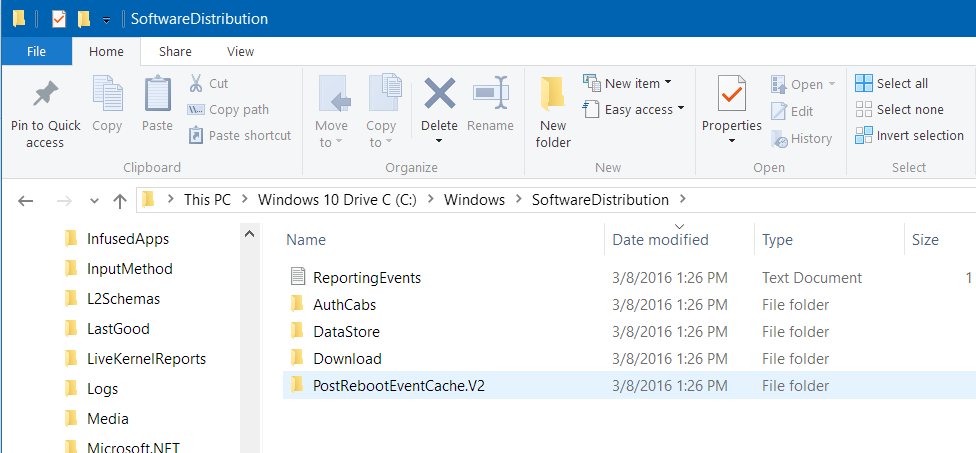 Once there and the windows update service has been stopped you can delete the entire contents of this folder. Once all the files have been deleted, restart the Windows Update service by executing this command from the command prompt.
Once there and the windows update service has been stopped you can delete the entire contents of this folder. Once all the files have been deleted, restart the Windows Update service by executing this command from the command prompt.
net start wuauserv
Immediately after you execute this command the windows update service will place the needed files in this directory once again.
2. The Temp Files Cache
Windows creates a directory used to hold temporary files. These are usually created as a result of system activity of various kinds, but these files are only needed for a short time. One of the failings of Windows is that these temporary files are often not deleted when they are no longer needed. Over time, a large amount of disk space can be used storing these files. The Disk Cleanup tool built-in to Windows can handle this clean-up for you.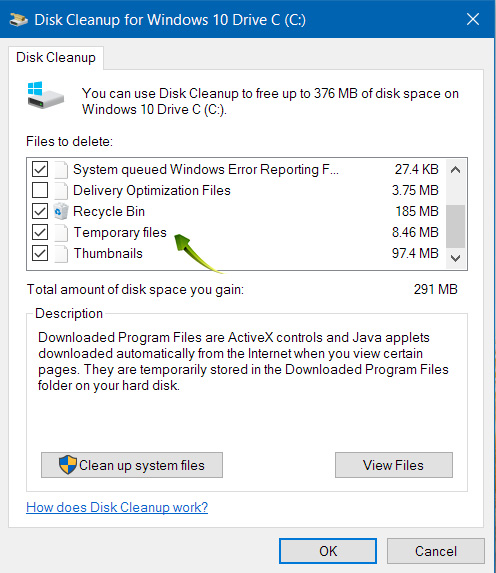
Open the Start Menu, search for the Disk Cleanup app, and launch it. When prompted, select the Windows drive (usually the C: drive). Windows will analyze your system and present you a series of file categories that can be deleted. Check the ones you want, but in particular, make sure the Temporary Files box is checked and click OK.
3. Thumbnail Cache
Windows creates thumbnails previews of video and image files to give you a graphic preview of individual files. Thumbnails are great from a usability standpoint, but over time, these can consume a fair bit of space on your hard drive.
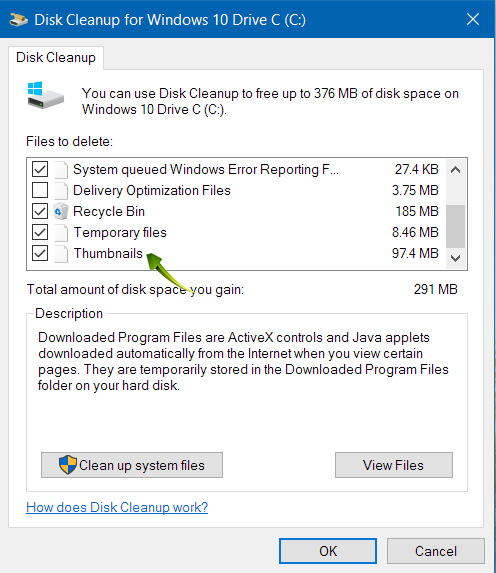
Again use the Disk Cleanup utility, and this time, check the Thumbnail box and click OK.
4. System Restore Cache
System Restore is a useful feature in Windows, although not as often used in the later versions of Windows since the reliability of Windows has improved dramatically. Be aware that System Restore uses a lot of disk space, because in order to function as designed it must save copies of all of the settings and variables that are necessary for a successful system restoration.
You can free up space by removing some of your restore points. You can also adjust the amount of space that is allocated or if you have an SSD drive some suggest disabiling this feature altogether.
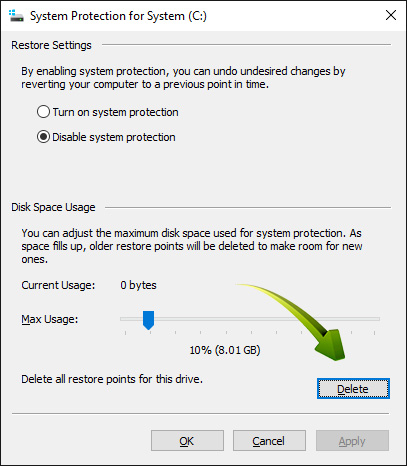 Again Open the Start Menu, search for the System app, and launch it. When it opens, look in the sidebar for the System Protection and make your selection.
Again Open the Start Menu, search for the System app, and launch it. When it opens, look in the sidebar for the System Protection and make your selection.
5. Windows Store Cache
When you use the Windows store to download apps, you should be aware that it will cache your downloads. This takes up space that you can safely recapture. Use the “WSReset” utility built into Windows to clear this cache.
To do this, open a Run prompt and enter WSReset.exe and click OK. A window will open and after a short time, the Windows Store will launch indicating that all is well and the Cache has been cleared. Keep in mind if you have an old system, this can take a minute or more.
