Start Windows 10 in Safe Mode
Most of you probably know, Safe Mode is a built-in troubleshooting feature of Windows which disables unnecessary drivers and programs during the startup process. By using Safe Mode will go a long way in determining if the problem is with a startup program or driver. If something is just not right when operating in normal mode, you can try Safe Mode. If the problem is not apparent when in safe mode, the problem is likely with one or more of the programs and/or drivers that have been added to your basic system configuration.
Method 1: Settings Menu – Advanced Startup
Open the Settings menu and select Update & Security; Recovery; Advanced Startup. Restart Now will restart your system in recovery mode, where you’ll encounter three options: Continue, Troubleshoot, or Turn off your PC.
Select Troubleshoot; Advanced Options. You’ll now have a range of new options as shown in the graphic below:
Click Startup Settings, followed by Restart. Your system will now restart. On reboot, you’ll meet the Startup Settings screen. You will be able to select the appropriate action from this point.
Method 2: Shift Restart
You can shorten the process of getting into Safe Mode by holding down Shift and clicking Restart under Power, in the Windows 10 Start Menu. This reboot will launch the recovery options, where you can select Troubleshoot; Advanced Options; Startup Settings.
Method 3: Modify System Configuration
Find the System Configuration panel using Cortana search. Search for system config, or msconfig. Once the System Configuration panel is open, select the Boot Tab. Simply select Safe Boot and Minimal. The next time you start your PC, it will start in Safe Mode.
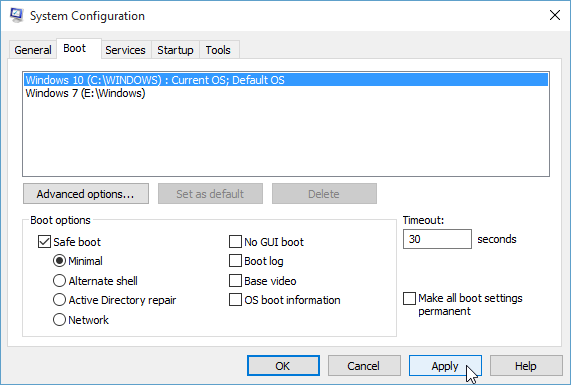 To return your system to normal operation simply uncheck all boxes from the boot dialog as shown above.
To return your system to normal operation simply uncheck all boxes from the boot dialog as shown above.
There are additional Safe Mode Options which you should be aware of as noted below:
- Minimal: Starts Safe Mode with the minimal amount of drivers and services, but with the Windows Graphical Interface.
- Alternate Shell: Starts Safe Mode with a Command Prompt, and without the Windows Graphical Interface. To use this mode you will need some basic knowledge of text commands. The mouse will not function in this mode.
- Active Directory Repair: Starts Safe Mode with the Windows graphical user interface in safe mode running critical system services and Active Directory.
- Network: Starts Safe Mode with the necessary services and drivers for networking, with the Windows Graphical Interface.
A more detail listing of all the MSCONFIG options can be found here!Using MSCONFIG

