Half-Duplex for Wifi and Full-Duplex for Wired Lan: Which is Better?
Duplex versus Simplex
In networking, the term Duplex signifies the ability for two devices to communicate with each other simultaneously. Simplex refers to unidirectional communication. In a Duplex communication system, both devices can transmit and receive information. Telephones and walkie-talkies are Duplex systems since they can both transmit and receive.
 On the other hand, simplex systems only permit one device to transmit information, while other receives. The hand held control of a hobbyist remote controlled car or airplane is an example of a Simplex system. The remote controlled car or airplane can only receive signals, but can not return them to the person holding the remote control.
On the other hand, simplex systems only permit one device to transmit information, while other receives. The hand held control of a hobbyist remote controlled car or airplane is an example of a Simplex system. The remote controlled car or airplane can only receive signals, but can not return them to the person holding the remote control.
Half-Duplex vs Full-Duplex
Full-Duplex communication between two components means that both can transmit and receive information between each other simultaneously. Telephones are Full-Duplex systems, since both parties on the phone can talk and listen at the same time. This is important for effective communication. Walkie-Talkies are examples of Half-Duplex systems, since you press the transmit key to talk, then release and wait for the other party to do the same.
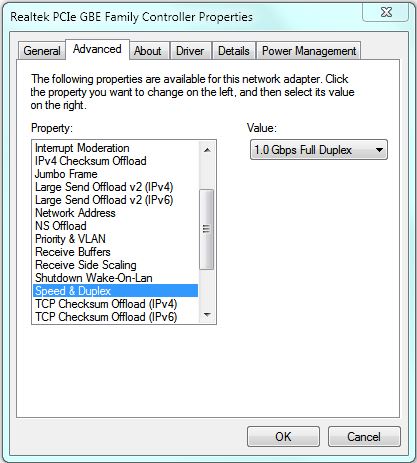
Lan Card – Full Duplex Property
When it comes to your computer, WiFi connections are running at Half-Duplex while the wired part of the LAN are on Full-Duplex. It is intuitive that Full-Duplex is more efficient and faster, and it is.
How Duplexing Affects WiFi Routers
WiFi routers are devices that modulate and schedule the flow of information to and from any WiFi-capable electronic device, such as your laptop, tablet or smartphone, to the Internet. This is done using a specific WiFi standard or protocol, such as 802.11a, 802.11b/g/n, and 802.11ac.
WiFi devices wirelessly connect to the router using radio waves at 2.4GHz or at 5GHz. The router schedules and makes sure the correct information flows between each connected device and the Internet; without collision and loss; by a process call Time Division Duplexing (TDD). This is done to simulate Full-Duplex communication.
TDD emulates Full-Duplexing by setting up or dividing time periods that alternate between transmission and reception. Data packets flow both ways as dictated by the time divisions. By chopping these time periods finely, devices connected this way seem to be transmitting and receiving simultaneously.
Well now you know! If you can connect your computer to your router with a Lan cable you should. You will have a more reliable and faster connection to your router and thus to the WWW.
For the technically interested, and thanks to Wikipedia, you can find more details here!Now go forth and impress your friends with your new expertise!